What sets the practice of facilitative leadership apart from other leadership types? What even is facilitative leadership?
In an era where the relationships between organizations, employees, and those in leadership positions keep getting more and more complicated with each passing day, finding the right leadership style for your team can be a real difference-maker.
While we will be going over the definition of facilitative leadership in detail, if you are a leader who enjoys implementing a culture of empowerment, nurturing talent, and developing new leaders, this is the right leadership style for you!
Before we go any further we would like to point out that this article is one in a series of posts on different leadership styles! You can find out more about other leadership styles by visiting the articles below:
- Democratic Leadership
- Authoritarian Leadership
- Affiliate Leadership
- Beurocratic Leadership
- 5 Levels of Leadership
We will be going over the meaning of facilitative leadership, the benefits a facilitative leadership style brings with it, alongside examples and case studies about facilitative leaders. We will also be analyzing the literature on the subject of different leadership styles in order to help you find the right leadership style for your organization!
Table of Contents
What is facilitative leadership?
Facilitative leadership is a management style that has a heavy emphasis on empowering employees. Above everything else, the facilitative leadership style prioritizes fostering open communication and collaboration as well as building a supportive work environment to optimize team performance.
The leader in facilitative leadership, as the name would suggest, has the role of a facilitator. This means the concepts of directing, controlling, and monitoring, take a back seat.
In this context, a leader’s primary responsibility is to create conditions that enable team members to collaborate effectively, make decisions together, and achieve their goals autonomously.
So… What sets facilitative leaders apart?
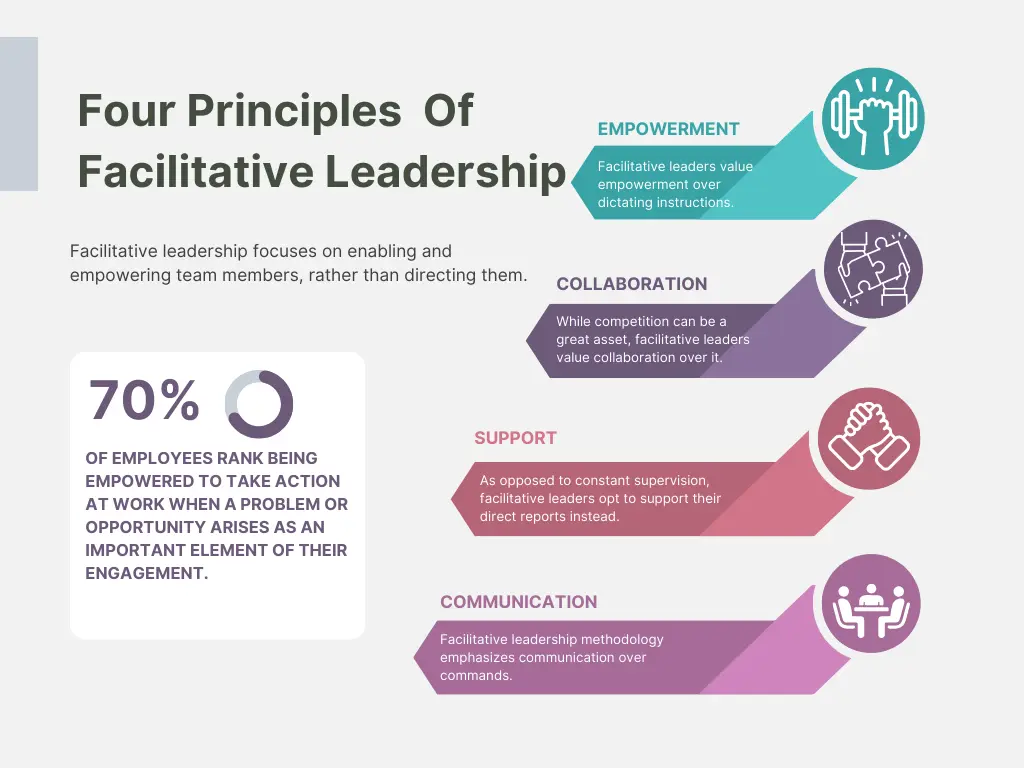
Empowerment over instruction
Facilitative leaders empower team members by providing them with the tools, resources, and authority needed to make decisions independently. This contrasts sharply with more authoritative styles where decisions are typically made at the top and instructions flow downward.
Collaboration over competition
This leadership style thrives on fostering a collaborative environment. Facilitative leaders work to ensure that all team members have a voice and feel valued in the decision-making process.
They encourage collective brainstorming and shared responsibilities, which differs from competitive environments where individuals vie for recognition and leadership positions.
Support over supervision
Instead of closely supervising every task, facilitative leaders focus on supporting team members. They provide guidance and feedback when needed but trust their team to manage their own tasks.
This support extends beyond just work-related issues to include professional development and personal growth, helping employees reach their full potential.
Communication over commands
Communication in facilitative leadership is bidirectional and open. Leaders communicate not to give orders but to facilitate understanding and cooperation.
They are also receptive to feedback and willing to adjust plans based on team input, which contrasts with more top-down, command-oriented leadership styles.
What are the benefits of facilitative leadership?
Proven Benefits of Facilitative Leadership
Facilitative leadership, with its emphasis on empowerment, collaboration, and support, offers several key benefits that contribute to both individual and organizational success. Research and practical evidence underscore the effectiveness of this leadership approach across various domains. Here are some of the most significant benefits:
Enhanced Team Creativity and Innovation
Facilitative leaders foster an open environment where team members feel safe to express innovative ideas and take creative risks. By encouraging diverse viewpoints and collaborative problem-solving, these leaders help cultivate a culture of innovation.
Anderson, De Dreu, and Nijstad found that supportive leadership that encourages participation and autonomy can enhance team creativity (Anderson, De Dreu, and Nijstad 147-173). Their study highlights how facilitative leadership by fostering an inclusive environment enables a higher level of creative output among team members.
Improved Employee Satisfaction and Engagement
One of the most notable benefits of facilitative leadership is its positive impact on employee satisfaction and engagement. According to Gallup’s research, managers who adopt a supportive and empowering leadership style can significantly influence employee engagement levels.
Their findings suggest that engaged teams show lower turnover, higher sales, and better profitability (Gallup). This supports the idea that facilitative leadership, which emphasizes empowerment and involvement, leads to higher employee satisfaction and engagement.
Better Conflict Resolution
The collaborative nature of facilitative leadership is particularly effective in conflict resolution. Simmons indicates that leadership styles focusing on collaboration and open communication, akin to facilitative leadership, are more effective in resolving conflicts within teams (Simmons 802-810).
These leaders facilitate discussions that allow for diverse viewpoints to be integrated and understood, reducing conflicts and improving team cohesion.
Increased Flexibility and Responsiveness
Organizations led by facilitative leaders are often more adaptable and responsive to changes. Since decision-making is decentralized and employees are encouraged to take initiative, these organizations can respond more quickly to market changes and challenges.
Heifetz, Grashow, and Linsky’s work on adaptive leadership highlights the importance of leaders facilitating adaptation to changing environments (Heifetz, Grashow, and Linsky).
This research underscores the need for leaders who empower their teams to respond swiftly and effectively to changes, a key component of facilitative leadership.
Long-term Organizational Success
Facilitative leadership contributes to the long-term success of organizations by building strong, autonomous teams that endure beyond the tenure of any single leader.
Bennis and Goldsmith discuss how leaders who focus on developing talent contribute to the sustainability of their organizations (Bennis and Goldsmith).
They argue that facilitative leaders, by investing in the growth and development of their team members, ensure that the organization remains resilient and prosperous in the long term.
Real cases where facilitative leaders made a difference:
Facilitative Leadership In The Tech Industry: Satya Nadella – Microsoft
When Satya Nadella became the CEO of Microsoft in 2014, he shifted the company culture from one of internal competition to a focus on collaboration, empathy, and a growth mindset.
Under Nadella’s leadership, Microsoft employees were encouraged to learn from failures and support one another, contrasting sharply with the previously rigid and competitive atmosphere.
Nadella’s display of a facilitative leadership approach led to significant increases in employee morale, innovation, and financial performance.
Facilitative Leadership In Non-profit Organizations: Wendy Kopp – Teach For America
Wendy Kopp, founder of Teach For America, exemplifies facilitative leadership in the non-profit sector. TFA’s model relies heavily on empowering young teachers to take initiative and lead educational reforms in their classrooms and communities.
Kopp’s leadership style involves facilitating these teachers’ growth through extensive training and support networks, enabling them to implement innovative teaching strategies and lead educational change effectively.
Facilitative Leadership In The Governmental Sector: Jacinda Ardern – Prime Minister of New Zealand
Jacinda Ardern, Prime Minister of New Zealand, has been noted for her facilitative leadership style, particularly in her handling of crises such as the Christchurch mosque shootings and the COVID-19 pandemic.
Ardern’s approach is characterized by empathy, open communication, and community involvement in decision-making processes.
Her leadership during the pandemic involved regular, transparent communications and a collaborative approach with health experts and the public.
The right tool for facilitative leadership
There is a wide array of tools available for performance management today for leaders to implement in their organization.
The key here is to use the right tools that support your brand of leadership.
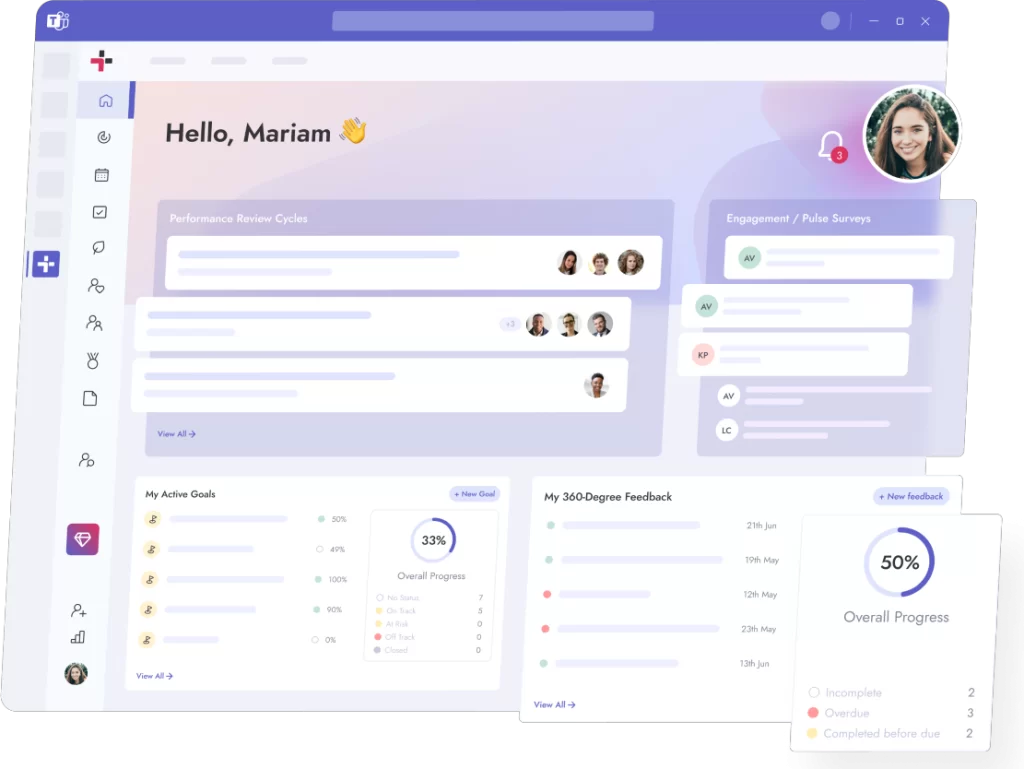
Facilitative leadership requires tools where employees own their goals, daily responsibilities, and are empowered to contribute to the decision making process.
This is where Teamflect can be the right tool for facilitative leaders. As a fully integrated performance management software for Microsoft Teams & Outlook, Teamflect helps leaders empower their employees in every facet of performance management:
Automated Goal Check-ins
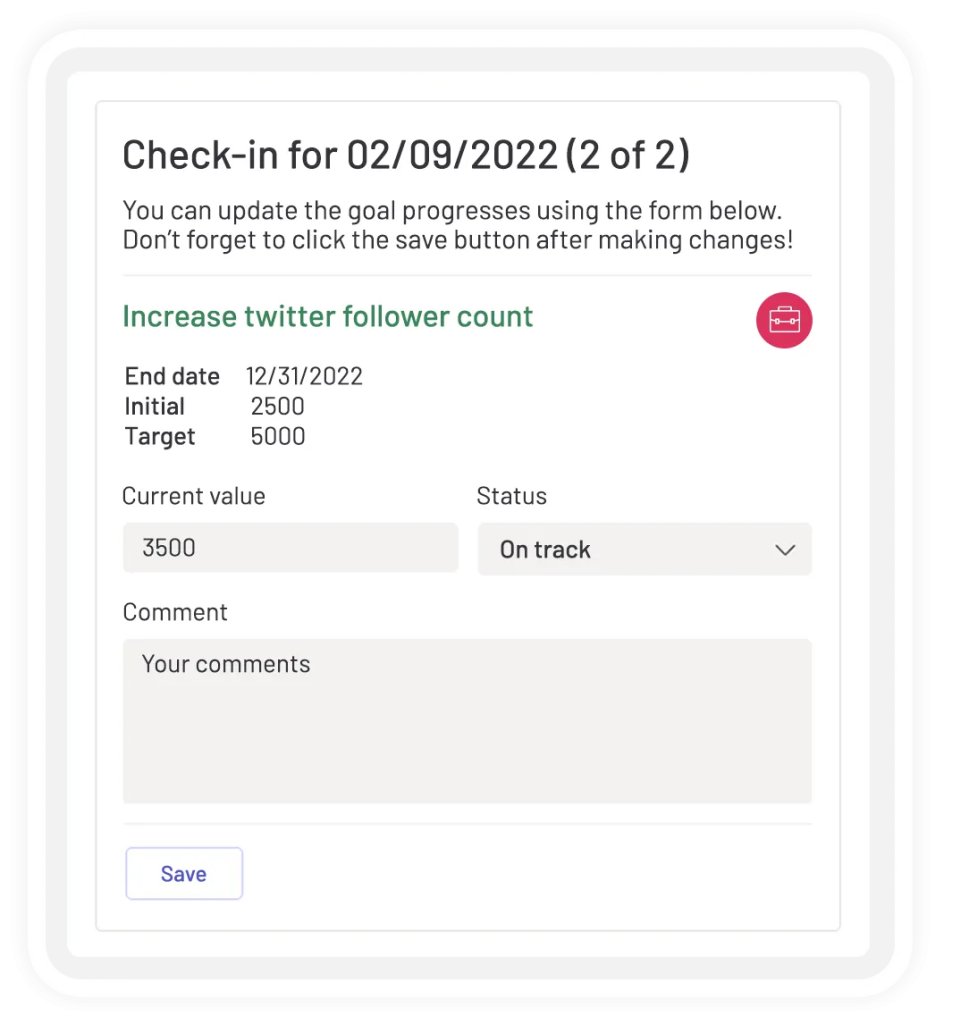
Goal owners in Teamflect are responsible for updating their own goal progression, without the need to be asked to do so by a manager.
Leaders can schedule automated goal check-ins to be scheduled at any interval of their choice. Goal owners receive automated goal check-in cards they can easily fill out through Microsoft Teams chat.
Goal owners can also edit their goals, update progress, attach files inside, leave comments, and more, making sure they have full autonomy in the goal-setting process.
Collaborative Meeting Agendas
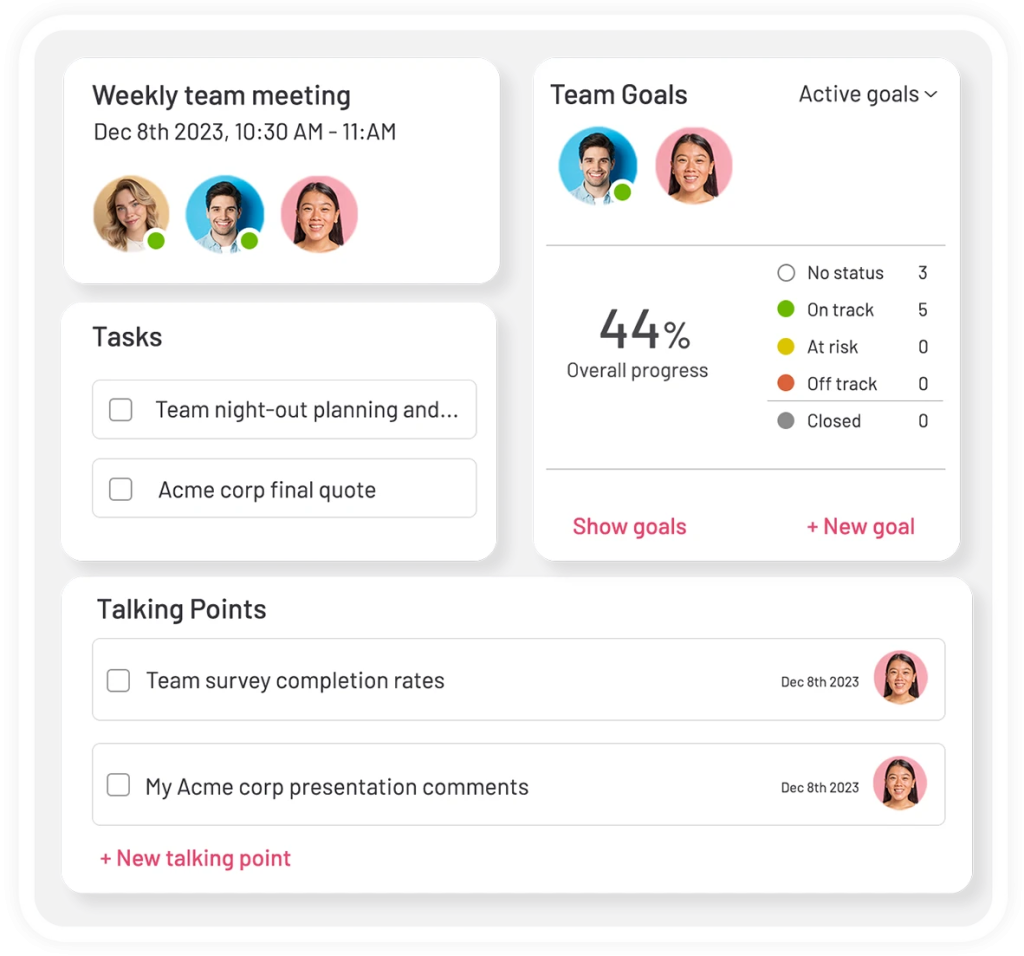
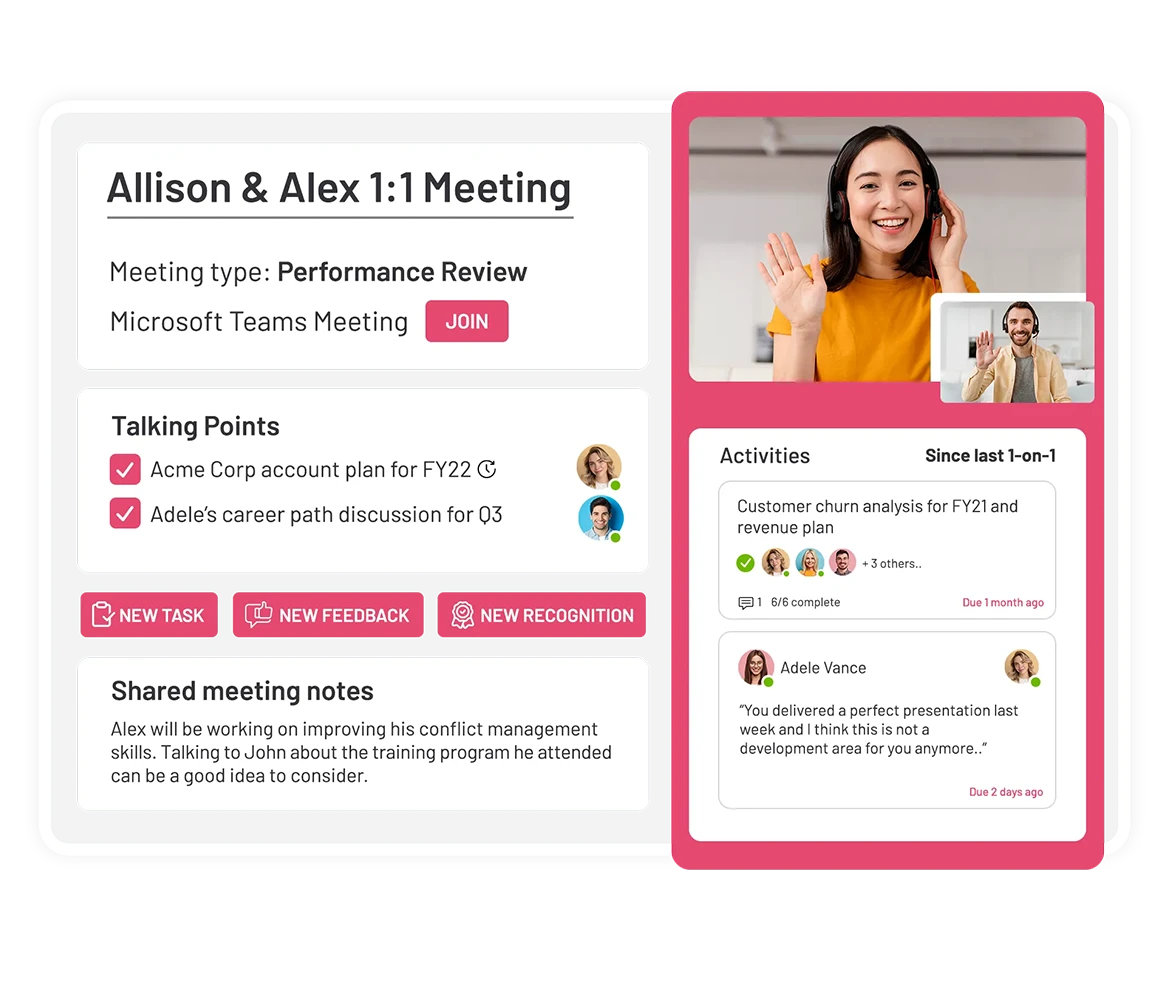
Whether you are having one-on-one or group meetings with your employees, give them the means to contribute to the meeting agenda with their own talking points and action items!
Convenient Pulse Surveys
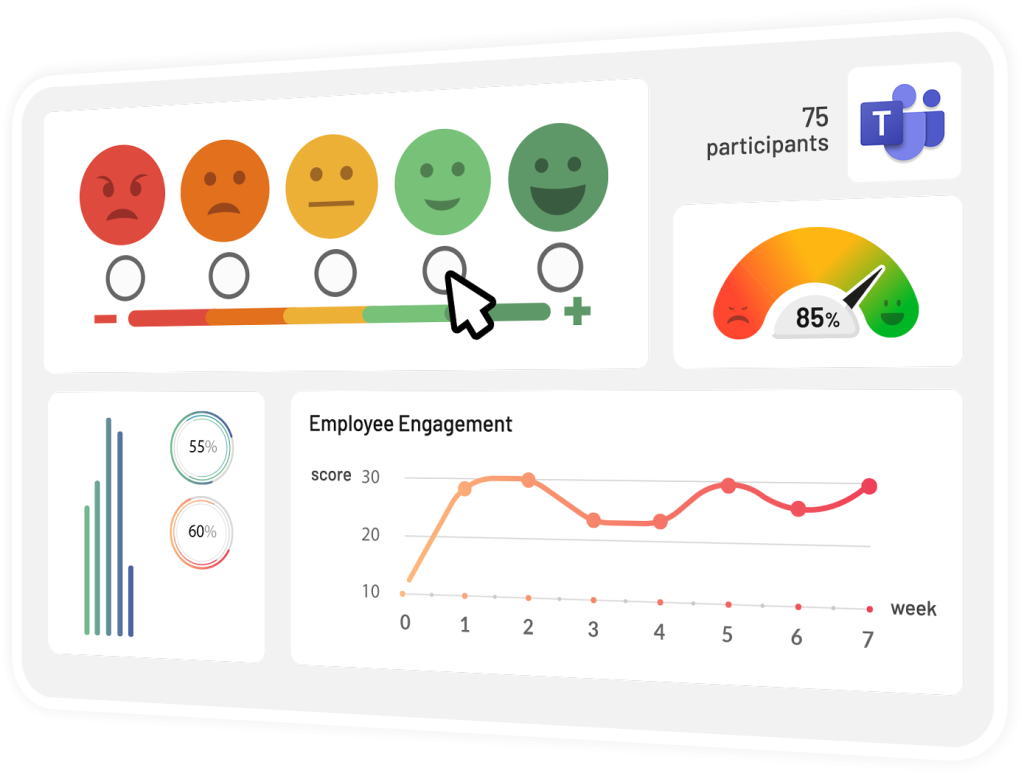
Giving your team a voice is the most important aspect of being a facilitative leader. One of the easiest ways to include your team in the decision-making process and gain their input on any matter is to conduct pulse surveys.
With an extensive library of customizable survey templates available to them, facilitative leaders can use Teamflect to not only listen to what their team has to say, but also to measure employee engagement and satisfaction scores.