Regardless of how the landscape of business may have been evolving over the years, one thing that hasn’t changed is the challenge of employee attrition rate. The circulation of talent in any organization is never purely statistical.
It reflects the combination of multiple factors such as workplace dynamics, culture, and employee satisfaction. This is why employee attrition rate is not simply an HR concern but rather something that comes alive in every aspect of the workplace at every level.
Let’s dive deeper into what employee attrition rate is, what it ideally should be, the root causes of why it may be higher or lower, and most importantly how you can play a part in tipping the scale. Whether you’re an HR professional or a business leader, discover the secrets of employee attrition rate with us!
Table of Contents
What Is The Employee Attrition Rate?
Employee attrition rate refers to the percentage of employees who choose to depart an organization over a certain period of time. It’s a vital metric that companies use to understand the rate at which employees decide to leave.
Understanding and tracking employee attrition rates will provide you with crucial insight into your business as it reflects the health of your workforce.
Depending on the outcome, you can get a variety of signals about whether the overall happiness with employee satisfaction, performance culture, leadership, compensation, and other elements such as career growth opportunities are at a good level in your workplace.
The ability to analyze and interpret the data you will be collecting will be the key to your success as a business in the long term. By following the employee attrition rate, you can see the real reasons behind talent departures, take proactive action, and implement retention strategies that will ultimately help create an attractive work environment that will actually be profitable.
How Can You Calculate The Employee Attrition Rate?
Typically the calculation for employee attrition rate comes from dividing the number of employees who leave within a specific time frame by the average number of employees during that same time frame.

To show by example, let’s say your company had 300 employees at the start of the year. You hired 50 more in that time and ended the year with a total of 320 employees, meaning that 30 people have left the company.
Number of employees who left = 30
Average number of employees = (300 + 320)/2=310
Attrition rate = (30/310) x 100 ≈ 9.68%
This indicates that approximately 9.68% of your workforce has left your organization during the year.
What Should Your Employee Attrition Rate Be?
There are many elements to consider when setting the benchmark for your company’s employee attrition rate. Unfortunately, there isn’t a universally set number for what the ideal should be. You will have to determine that yourself. Make sure to consider details specific to your company and your specific circumstances when doing so. However, a relatively low rate should be your main aim in this case.
A low attrition rate is associated with a stable and happy work environment. While we can’t give you a fixed number for this, we can tell you a few things to factor in when setting your goal.
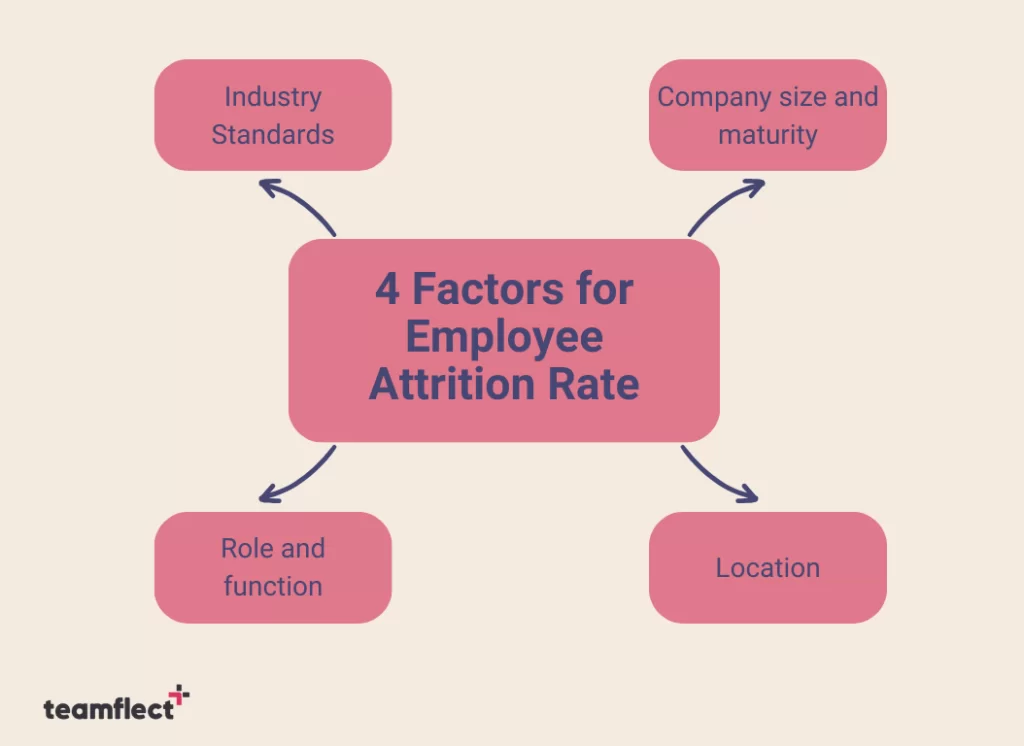
- Industry Standards: Various industries will have various attrition rates. Industries with a high demand for specialization might have a higher turnover for example.
- Company Size and Maturity: If you have a smaller and newer company, you may experience higher attrition rates as you’re newly establishing your culture and other processes.
- Role and Function: Certain roles of departments may have different attrition rates depending on the specific nature of the role such as job market demand or stress levels etc.
- Location: Employee attrition rate may also vary depending on your region or country with regard to the overall economic conditions.
While these are important elements to consider when setting the bar for your own employee attrition rate, don’t forget that each company is likely to have its own experience and it is more valuable to consider the overall trend within your establishment.
That way you can actually consider your own history and your own benchmarks when making interpretations with regards to the success of your organization. This will give you a clearer path to follow as you understand more about the underlying reasons for the data you’ve collected and maintain a healthy business.
What Is A High Employee Attrition Rate?
A high attrition rate is when the employee attrition rate exceeds the average rate of your expectation according to your industry, company size, and geographical region. It’s a relative term that depends on various reasons.
As we mentioned, there is no universally agreed upon rate and you will have to interpret according to your specific benchmarks if the employee attrition rate is high or not. However, here’s a general guide as to what you can consider:
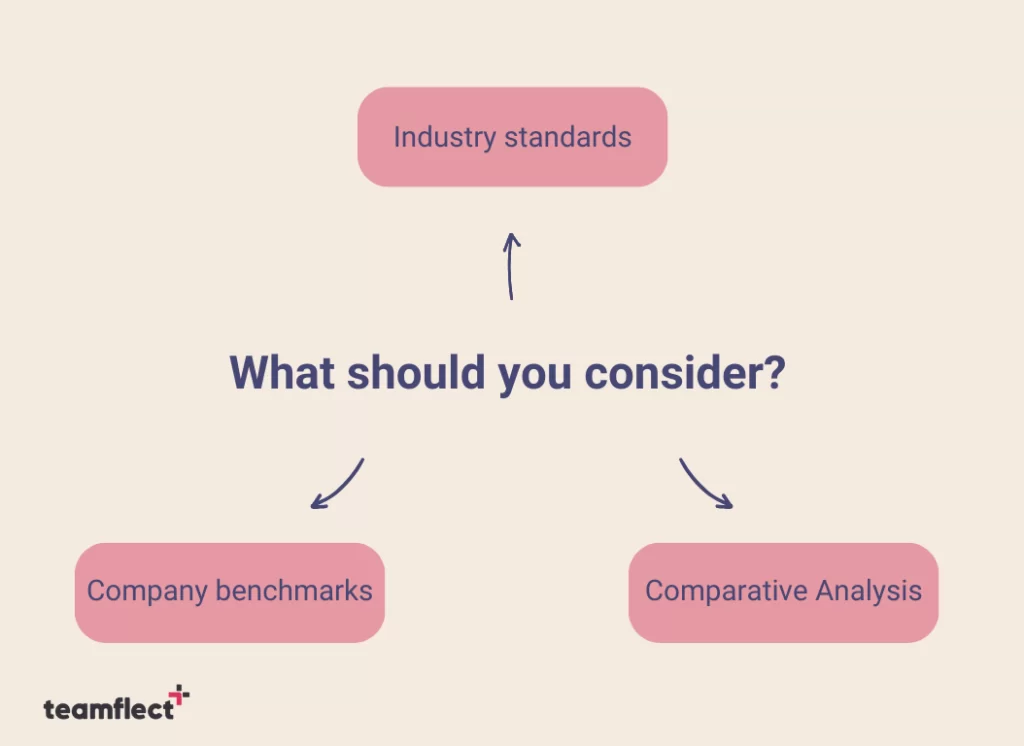
- Industry Standards: The nature of the work you do in your industry is likely to affect what you consider a high or low employee attrition rate.
- Company Benchmarks: You will establish your own benchmarks according to company-specific history. An attrition rate that is significantly higher than previous data will be considered too high for you.
- Comparative Analysis: Comparison with other companies in your industry can provide valuable information as to where you should stand with employee attrition rate. It should also be considered that when doing such an analysis either within your own historical data or between your company and others, consider what other factors were part of your reality within that certain time frame.
What Causes A High Employee Attrition Rate?
A high employee attrition rate can stem from a variety of reasons. This is where it becomes considerably less statistical. Here are some factors to consider when you’re interpreting a high employee attrition rate:
- Work Culture: An unsupportive work environment with possibly a lack of recognition or ineffective management can cause dissatisfied employees.
- Career Growth Opportunities: Employees are highly likely to seek career growth prospects either within or outside of their current organization. It is important to leave room for opportunities that will keep your employees satisfied.
- Benefits and Compensation: Poor benefits and compensation that aren’t competitive are some of the most important reasons that employees may seek other positions.
- Workload: Excessive workload or unrealistic expectations can play into burnout and will affect whether employees wish to stay or not.
- Leadership: An unsupportive or ineffective leader will severely hurt trust and motivation in the workplace.
- Work-Life Balance: An imbalance in this case can lead to severe dissatisfaction, hence contributing to the choice to leave.
- Job Roles: Employees may choose to depart due to a mismatch between their roles and the actual responsibilities that are held against them in their day to day.
- Diversity and Inclusion: If a workspace is inclusive it creates a sense of belonging. One that misses this quality is more likely to drive employees out of the company.
By addressing any problems that you might be facing regarding these aspects, you can create an environment at your organization that numerically matches your vision of a successful business.
Attrition vs. Turnover
Attrition and turnover are concepts that are related to one another with refined differences in what they represent within the context of workforce management.
Attrition: Attrition specifically refers to the natural reduction in a company’s workforce
over time. This can occur due to voluntary departures, retirements, resignations, and others like reaching the end of a contract. It includes both voluntary and involuntary occasions with a general focus on voluntary ones.
Turnover: Turnover on the other hand is more of an unbrella term in this case. Turnover rate includes not just departures from the company but also any other changes to the company in terms of workforce. This would mean any voluntary or involuntary departures, as well as any new hires in that process.
All in all, attrition is a term within turnover. It is specifically related to departures from an organization in the natural sense while turnover encompasses all shifts, departures, and replacements. It is a sum of all workforce movements within your workplace.
Attrition vs. Retention
When it comes to attrition and retention, they are more so the two sides of the same coin.
Attrition: Employee attrition is the number of employees that leave an organization. It is the rate at which these employees are no longer part of the company’s workforce due to a variety of reasons.
Retention: Retention focuses more on the strategies that are in place to keep employees within the workforce. It means creating such an environment where the workforce would have a positive association with the company overall so that they choose to stay rather than leave the workforce.
Overall, attrition refers to departures whilst retention keeps the attritions down. The lower the attrition rate, the better the retention strategies.
How To Reduce The Employee Attrition rate?
In order to reduce the employee attrition rate, you’ll have to implement several strategies in your workspace to make sure you have a supportive, engaging, and fulfilling environment.
Here Are Some Answers:
- Onboarding Processes: Ensure a smooth onboarding process that successfully introduces new teammates to your company culture, values, and roles. Setting clear expectations in this stage and providing proper training can set you up with a long and happy commitment.
- Benefits and Compensation: Make sure to regularly review and adjust salaries and benefits to make sure you remain relevant and competitive in the landscape you operate in. Consider aligning with what your employees’ needs and preferences are when setting your benefits.
- Growth Opportunities: Offering pathways to developing skills and advancements in their careers is a very important part of keeping your workforce satisfied and motivated.
- Positive Work Culture: Create a supportive environment for your employees. One where they feel recognized, valued, engaged, and motivated. Promote open communication and trust to sustain it.
- Good Leadership: Invest in finding ways to improve leadership within your organization so that you’re equipped to support and guide your employees at all levels, per the needs of the departments.
- Monitor Data: Keep tracking and collecting data so that you can identify patterns and the areas where you can set newer strategies.
- Use Teamflect: Use Teamflect, the best performance management software already implemented in Microsoft Teams! Let us assist you in all your daily tasks, setting goals for the future, and keep you connected! Teamflect will allow you to keep track of your workspace at all levels and assist you in your endeavors to keep attrition rates low, and your business successful with ease.